If you’re worried about how cardio and cortisol are affecting your waistline, you’ve probably noticed a frustrating pattern: the harder you redline your engine, the more that stubborn belly fat seems to stick around like a bad houseguest. It’s the ultimate fitness betrayal. You put in the work, you sweat through the shirts, and you skip the pizza—yet the scale doesn’t budge, and you feel like a walking zombie.
Most guys think the answer is more intensity. They think they just need to “embrace the suck” for another 45 minutes on the treadmill. But for many of us, especially as we get older, that extra mile isn’t burning fat; it’s fueling a hormonal fire that keeps us soft and stressed. This isn’t just about “getting in shape”—it’s about understanding the delicate biological balance between exertion and recovery.
📌 Key Takeaways: The TL;DR
- Cortisol isn’t the enemy: It’s a vital hormone for energy, but chronic elevation from overtraining causes muscle loss and fat storage.
- The 60-Minute Rule: Intense cardio sessions lasting longer than an hour often trigger a massive cortisol spike that overrides fat burning.
- HIIT vs. LISS: High-intensity training is a tool, not a lifestyle. Low-intensity steady-state (LISS) cardio is actually your best friend for lowering baseline stress.
- The “Wired but Tired” Trap: If you can’t sleep after a hard workout, your cortisol curve is broken.
- Nutrition Matters: Eating carbs and protein immediately after cardio can “turn off” the stress response.
The Grind That’s Not Working: Why Your Routine Might Be Backfiring
We live in a culture that worships the “no pain, no gain” mentality. We see the Instagram influencers screaming about “outworking the competition.” But here’s the cold, hard truth: your body doesn’t care about your “hustle.” It cares about survival.
According to the Mayo Clinic, while exercise is a proven stress-buster, it is also a physical stressor in itself. When you push your body through grueling, high-intensity cardio day after day, your brain senses a threat. It doesn’t know you’re trying to fit into a smaller pair of jeans; it thinks you’re being chased by a predator for three hours a week. In response, it pumps out cortisol.
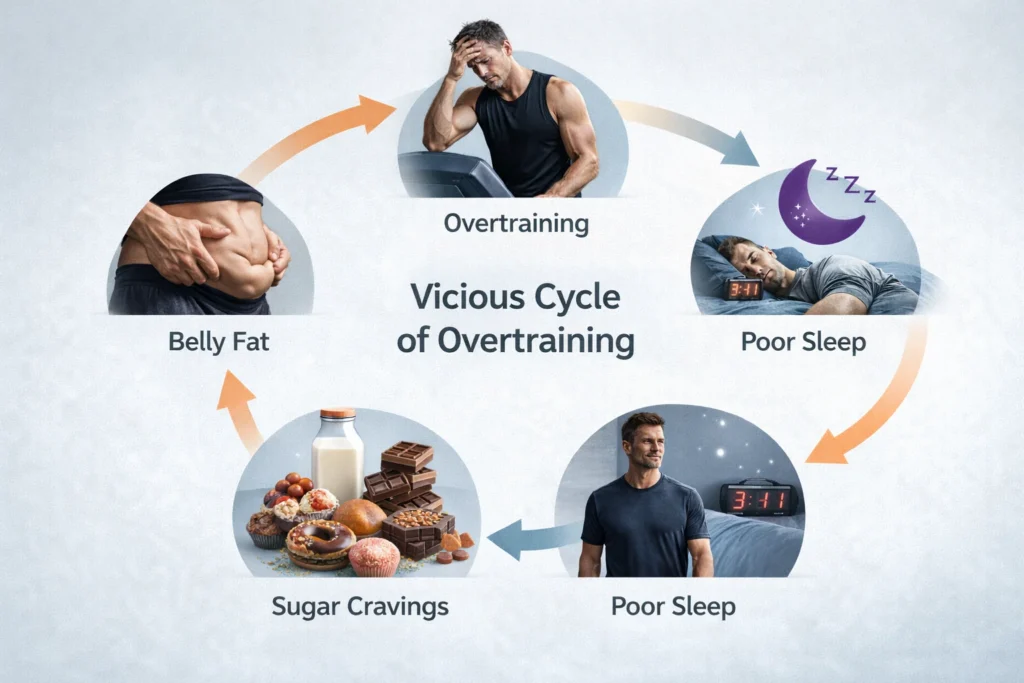
This isn’t a problem if it happens once in a while. But when it becomes chronic, your body enters a “protective” mode. It starts holding onto fat—specifically visceral fat around your organs—and starts breaking down your hard-earned muscle for quick energy. This is why you see guys who run 30 miles a week but still have a “spare tire” and zero muscle definition.
🏃♂️ The Prime Perspective
Back in my late 30s, I hit a wall. I was training for a tactical fitness challenge and figured that if three days of HIIT was good, six days must be better. I was doing hill sprints on my “off” days and finishing every lift with a 20-minute Metcon. Within a month, I was ‘wired but tired.’ I’d lay in bed at 11 PM with my heart racing like I’d just had a double espresso, but I had no strength in the gym the next morning.
My joints ached, my mood was trash, and—infuriatingly—I actually gained two pounds of fat around my midsection. I was suffering from overtraining syndrome, and my cortisol levels were through the roof. It wasn’t until I cut my ‘hard’ cardio back to twice a week and started going for long, boring walks that my body finally relaxed and the fat started to drop. It was a lesson in humility: you can’t out-train a hormonal mess.
What is Cortisol? (And Why It’s Not the Enemy)
Before we trash-talk cortisol, we need to understand that we’d be dead without it. Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced by your adrenal glands. It’s often called the “stress hormone,” but it’s actually your “get stuff done” hormone.
In a healthy system, cortisol follows a circadian rhythm. It peaks in the early morning to help you wake up and feel alert, and it gradually drops throughout the day so you can fall asleep at night. During a workout, cortisol rises to help mobilize blood sugar (glucose) and fat so your muscles have fuel.
This process is managed by the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis. Think of it as a biological handshake: Your brain’s hypothalamus signals the pituitary gland, which then tells your adrenals to release the floodgates. It’s a beautifully orchestrated system—until we start screaming at it with too much high-intensity training.
The problem starts when that spike never comes down. If you have a high-stress job, poor sleep, and then you layer on 90 minutes of “chronic cardio,” your adrenal glands stay in overdrive. This constant flood of cortisol leads to overtraining syndrome and a host of metabolic issues.
The Cardio and Cortisol Paradox: Acute vs. Chronic
| Feature | Acute Cortisol (Healthy) | Chronic Cortisol (Harmful) |
| Duration | Short-term (minutes/hours) | Long-term (weeks/months) |
| Metabolic Effect | Mobilizes fat for fuel | Stores visceral (belly) fat |
| Muscle Effect | Temporary breakdown/repair | Progressive muscle wasting |
| Mood | Focus and alertness | Anxiety and irritability |
The Impact of Intensity: How Cardio Choice Affects Cortisol
The relationship between cardio and cortisol isn’t binary. It’s not “cardio is bad” or “cardio is good.” It’s about the dose and the intensity. Harvard Health notes that while aerobic exercise is vital for heart health, the psychological and physical “cost” of that exercise varies wildly depending on how hard you push.
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training)
HIIT is like a drug. In small doses (1–2 times per week), it’s incredibly effective for boosting your VO2 max and burning fat. But because it’s so intense, it triggers a massive release of cortisol. If you do HIIT every day, you’re essentially keeping your body in a state of high-alert 24/7. This is one of the most common fitness mistakes men make.
LISS (Low-Intensity Steady-State)
Walking, light cycling, or swimming at a casual pace doesn’t put the same strain on the central nervous system. In fact, LISS cardio can actually lower your baseline cortisol levels by activating the parasympathetic nervous system (your “rest and digest” mode).
This is why a 30-minute walk in nature is often more effective for fat loss than a 30-minute sprint session for a guy who is already stressed out.
💡 What Most Guys Miss
Most articles tell you that cortisol causes fat storage, but they don’t explain why it targets the belly. Visceral fat cells (the deep fat around your organs) have four times more cortisol receptors than subcutaneous fat (the fat under your skin). When cortisol is high, it literally ‘drags’ fat from other parts of your body and deposits it in your abdomen. This isn’t just an aesthetic issue; visceral fat is metabolically active and pumps out inflammatory chemicals that can lead to insulin resistance and lower testosterone.
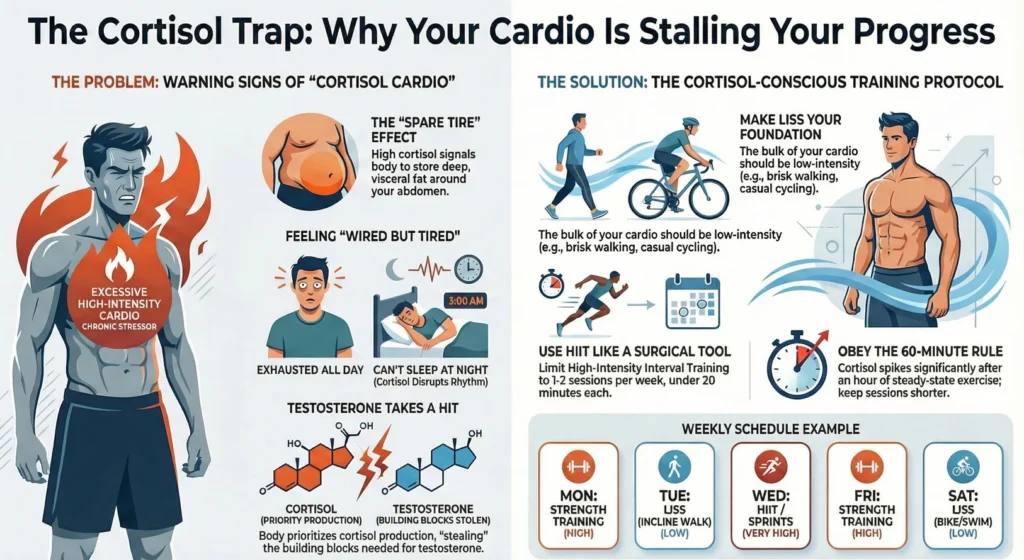
Are You Doing “Cortisol Cardio”? The 5-Point Self-Assessment
If you’re worried your routine is hurting you, look for these five “red flags.” If you check more than three, it’s time to pivot.
1. The “Spare Tire” That Won’t Deflate
You’re losing muscle in your arms and legs, but your waist circumference is staying the same or increasing. This is a classic sign of high cortisol belly fat storage.
2. Sleep Sabotage
You feel exhausted all day, but as soon as your head hits the pillow, your brain starts a marathon. You might also wake up at 3 AM wide awake. This happens because your evening cortisol levels are failing to drop, keeping you in a sympathetic “fight-or-flight” state.
3. The Mid-Afternoon Crash
You need a third cup of coffee at 2 PM just to survive the workday. This “wired but tired” feeling is a hallmark of HPA axis dysregulation.
4. Chronic Cravings
You find yourself standing in front of the pantry at 9 PM craving sugar, salt, and fat. This is cortisol telling your brain it needs “emergency fuel.”
5. Stalled Progress
Your progressive overload has stopped. You aren’t getting faster or stronger, even though you’re training harder. Your body is too busy trying to survive to bother with building new tissue.
The Hormonal Cascade: How High Cortisol Hijacks Your Body
When your cortisol is chronically high, it doesn’t just affect stress; it starts a domino effect across your entire hormonal system.
The Insulin Connection
High cortisol tells your liver to dump glucose into your bloodstream for quick energy. But if you aren’t actually fighting a tiger, that glucose has nowhere to go. Your body releases insulin to clear the sugar. Over time, this leads to insulin resistance. This is why losing fat feels impossible—your body is stuck in a cycle of high sugar and high insulin, which is the perfect recipe for fat storage.
The Hunger Hormone Hijack
Ever notice how a long, grueling run makes you want to eat everything in sight? That’s because cortisol suppresses leptin (the hormone that tells you you’re full) and spikes ghrelin (the hormone that tells you you’re hungry). This isn’t just about willpower; it’s about neurobiology. When cortisol is elevated, it activates the brain’s reward centers, making highly palatable ‘junk’ foods look like a life raft in a stormy sea.
The Testosterone Tank
Cortisol and testosterone are made from the same raw material (pregnenolone). When you are constantly stressed, your body prioritizes cortisol production over testosterone. This is known as the “pregnenolone steal.” If you want to boost testosterone naturally, the first step isn’t a supplement; it’s managing your stress.
Your Action Plan: The Cortisol-Conscious Training Protocol
So, how do you do cardio without wrecking your hormones? It comes down to balance. We need to move away from “chronic cardio” and toward “strategic movement.”
Step 1: Make LISS Your Foundation
The bulk of your “cardio” should be low-intensity. Aim for 3–5 sessions a week of Zone 2 training. This is a pace where you can comfortably hold a conversation without gasping for air.
- Examples: Brisk walking on an incline, casual cycling, or using the elliptical at a moderate pace.
- Duration: 30–45 minutes.
Step 2: Use HIIT Like a Surgical Tool
HIIT is powerful, but it’s high-stress. Limit your high-intensity sessions to once or twice a week.
- Rule: Keep the total work time (excluding warm-up) under 20 minutes.
- Rule: Never do HIIT on a day when you’ve had less than 6 hours of sleep.
Step 3: Prioritize Strength Training
If you have to choose between a run and a lift, choose the lift. Strength training improves your insulin sensitivity and builds muscle, which makes your body more resilient to cortisol spikes.
Step 4: Watch the Clock
Cortisol naturally begins to climb significantly after about 60 minutes of steady-state exercise. If you’re a recreational athlete, there is rarely a reason to do cardio for longer than an hour. If you’re training for a marathon, you need to be extremely diligent about your recovery and rest.
| Day | Activity Type | Duration | Intensity |
| Mon | Strength Training | 45-60 min | High (Lifting) |
| Tue | LISS (Incline Walk) | 30-45 min | Low (Zone 2) |
| Wed | HIIT / Sprints | 20-25 min | Very High |
| Thu | Active Recovery | 20 min walk | Very Low |
| Fri | Strength Training | 45-60 min | High (Lifting) |
| Sat | LISS (Bike/Swim) | 60 min | Low (Zone 2) |
| Sun | Full Rest | N/A | None |
Fueling for Resilience: Post-Workout Nutrition
One of the biggest mistakes guys make is finishing a hard cardio session and then waiting two hours to eat “to keep the fat burning going.” This is a disaster for cortisol.
When you finish a workout, your cortisol is at its peak. To bring it down, you need to signal to your body that the “threat” is over. The best way to do that? Carbohydrates and protein.
A small post-workout meal (like a protein shake and a banana) triggers an insulin spike. In this specific context, insulin is actually good—it acts as an “off switch” for cortisol and starts the repair process for your muscles. Adding magnesium for testosterone can also help calm the nervous system after a hard session.
✅ Your 24-Hour Action Plan
- Step 1: Swap your next HIIT session for a 45-minute brisk walk. Monitor how your energy feels the next morning.
- Step 2: Eat 30-50g of carbohydrates within 60 minutes of your next hard workout to blunt the cortisol response.
- Step 3: Track your resting heart rate (RHR) upon waking. If it’s 5-10 beats higher than usual, take a full rest day—your cortisol hasn’t cleared yet.
The Bottom Line: Train Smarter, Not Harder
The myth that you need to kill yourself on the treadmill to lose fat is one of the most damaging lies in fitness. If you’re a man over 30, your hormonal health is far more important than your “mile time.”
By balancing your cardio and cortisol, you aren’t just losing fat; you’re gaining energy, improving your sleep, and protecting your testosterone. Stop trying to outrun your stress. Start moving in a way that makes your body feel safe, strong, and resilient.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cardio and Cortisol
Does all cardio increase cortisol?
Yes, all physical activity increases cortisol to some degree because exercise is a form of stress. However, low-intensity cardio (like walking) causes a very small, manageable increase, whereas high-intensity or very long cardio (over 60 minutes) causes a much larger spike.
How can I tell if my cortisol is high from exercise?
Common signs include persistent fatigue, an inability to fall asleep (the “wired but tired” feeling), increased belly fat even when dieting, and a lack of motivation to train. You can also track your Heart Rate Variability (HRV); a consistently low HRV often indicates that your body is stuck in a high-cortisol, sympathetic state.
Is HIIT bad for cortisol levels?
HIIT isn’t “bad,” but it is very demanding. It triggers a significant cortisol release to help the body handle the extreme intensity. It only becomes a problem when you do it too frequently (more than 2–3 times a week) without enough recovery time.
Can I do cardio on an empty stomach?
Fasted cardio can be a double-edged sword. While it may slightly increase fat oxidation, it also significantly increases the cortisol response because the body has to work harder to mobilize energy without incoming fuel. For most men, a small pre-workout snack is better for hormonal health.
What is the best type of cardio for fat loss?
For long-term fat loss, a combination of strength training (to build muscle) and low-intensity steady-state (LISS) cardio (to burn calories without spiking stress) is usually the most effective approach for men concerned about cortisol.








